没打,王哥发了我三题,我就看了一下,稍微多花了时间。
CSGO
这题golang写的,打开看到一个base64表和密文,直接解码不对,估计换表了,然后有反调试。没怎么找,直接就运行后attach上去
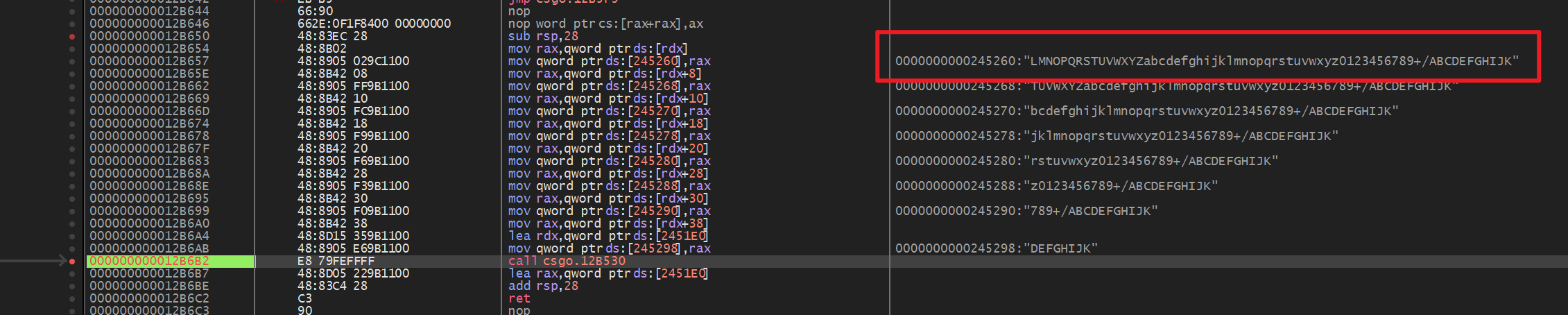
拿到base表就直接秒了
vm_co
虚拟机题,不是很难,这是赛后看的,就完整翻译了一遍
Rip = 0
def function_17(x, y):
global Rip
if x == 0:
Rip = y
return f"cmp x, 0\n jz {Rip}"
def function_18(x, y):
global Rip
if x:
Rip = y
return f"cmp x, 0\n jnz {Rip}"
def function_19(x, _):
global Rip
Rip = x
return f"jmp {x}"
vm_opcode = {
"0": lambda x, y: f"swap(vm_body[{x}], vm_body[{y}])",
"1": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] ^= vm_body[{y}]",
"2": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] += {y}",
"3": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] += vm_body[{y}]",
"4": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] -= {y}",
"5": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] -= vm_body[{y}]",
"6": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] *= {y}",
"7": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] *= vm_body[{y}]",
"8": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] = vm_body[{x}] / {y}",
"9": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] = vm_body[{x}] / vm_body[{y}]",
"10": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] = vm_body[{x}] % {y}",
"11": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] = vm_body[{x}] % vm_body[{y}]",
"12": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] <<= {y}",
"13": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] = vm_body[0] << {y}",
"14": lambda x, _: f"vm_body[Var1 + 16] = vm_body[{x}]\n Var1 += 1",
"15": lambda x, _: f"print(vm_body[{x}])",
"16": lambda _, __: f"Var1 -= 1\nprint(vm_body[Var + 16])",
"17": function_17,
"18": function_18,
"19": function_19,
"20": lambda x, _: f"t = vm_body[ vm_body[{x}] ]\n vm_body[Var + 16] = t\nVar += 1",
"21": lambda _, __: f"Var1 -= 1\n vm_body[0] = vm_body[Var + 16]",
"22": lambda x, _: f"vm_body[Var + 16] = {x}\nVar += 1",
"23": lambda _, __: f"if Rip >= 15:\n\tbreak\ncontinue",
"24": lambda _, __: f"vm_body[0] = vm_body[2] | vm_body[1]",
"25": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] = vm_body[0] >> {y}",
"26": lambda x, y: f"vm_body[{x}] = {y}",
}
def interpre_byte_code(opcodes: list, len: int):
global Rip
Rip = 0
while Rip < len:
# print(f"rip => {Rip}")
print(vm_opcode[str(opcodes[Rip])](opcodes[Rip + 1], opcodes[Rip + 2]))
Rip += 3
opcode1 = list(0x20D01011903001A.to_bytes(8, "little"))
opcode2 = list(0x300010201180702.to_bytes(8, "little"))
opcode3 = opcode1[:7] + opcode2
opcode3[2] = "flag[i]"
print(opcode3)
interpre_byte_code(opcode3, 15)
opcode1 = list(0x20D02011903001A.to_bytes(8, "little"))
opcode2 = list(0x400010201180602.to_bytes(8, "little"))
opcode3 = opcode1[:7] + opcode2
opcode3[2] = "vm_body[0]"
interpre_byte_code(opcode3, 15)
opcode1 = list(0x20D03011903001A.to_bytes(8, "little"))
opcode2 = list(0x500010201180502.to_bytes(8, "little"))
opcode3 = opcode1[:7] + opcode2
opcode3[2] = "vm_body[0]"
interpre_byte_code(opcode3, 15)
opcode1 = list(0x20D04011903001A.to_bytes(8, "little"))
opcode2 = list(0x600010201180402.to_bytes(8, "little"))
opcode3 = opcode1[:7] + opcode2
opcode3[2] = "vm_body[0]"
interpre_byte_code(opcode3, 15)
翻译出来的结果
[26, 0, 'flag[i]', 25, 1, 1, 13, 2, 7, 24, 1, 2, 1, 0, 3]
vm_body[0] = flag[i]
vm_body[1] = vm_body[0] >> 1
vm_body[2] = vm_body[0] << 7
vm_body[0] = vm_body[2] | vm_body[1]
vm_body[0] ^= vm_body[3]
vm_body[0] = vm_body[0]
vm_body[1] = vm_body[0] >> 2
vm_body[2] = vm_body[0] << 6
vm_body[0] = vm_body[2] | vm_body[1]
vm_body[0] ^= vm_body[4]
vm_body[0] = vm_body[0]
vm_body[1] = vm_body[0] >> 3
vm_body[2] = vm_body[0] << 5
vm_body[0] = vm_body[2] | vm_body[1]
vm_body[0] ^= vm_body[5]
vm_body[0] = vm_body[0]
vm_body[1] = vm_body[0] >> 4
vm_body[2] = vm_body[0] << 4
vm_body[0] = vm_body[2] | vm_body[1]
vm_body[0] ^= vm_body[6]
这是每一个字符单独的加密过程,非常简单,就是字节的bit变换,逆过来就是exp
exp:
c = [
0xDF,
0xD5,
0xF1,
0xD1,
0xFF,
0xDB,
0xA1,
0xA5,
0x89,
0xBD,
0xE9,
0x95,
0xB3,
0x9D,
0xE9,
0xB3,
0x85,
0x99,
0x87,
0xBF,
0xE9,
0xB1,
0x89,
0xE9,
0x91,
0x89,
0x89,
0x8F,
0xAD,
]
d = list(0xBEEDBEEF.to_bytes(4, "little"))
def enc(x: int):
t = ((x >> 1) | (x << 7)) & 0xFF
t ^= d[0]
t = ((t >> 2) | (t << 6)) & 0xFF
t ^= d[1]
t = ((t >> 3) | (t << 5)) & 0xFF
t ^= d[2]
t = ((t >> 4) | (t << 4)) & 0xFF
t ^= d[3]
t = ((t >> 5) | (t << 3)) & 0xFF
return t
def dec(x: int):
t = ((x >> 3) | (x << 5)) & 0xFF
t ^= d[3]
t = ((t >> 4) | (t << 4)) & 0xFF
t ^= d[2]
t = ((t >> 5) | (t << 3)) & 0xFF
t ^= d[1]
t = ((t >> 6) | (t << 2)) & 0xFF
t ^= d[0]
t = ((t >> 7) | (t << 1)) & 0xFF
return t
c = [dec(i) for i in c]
print(bytes(c))
ez_加密
中间加了很多混淆,很怪的混淆,我抽象出来大概是这样的一个形式
/* return flag + 1 + input; */
int core(int flag, int input)
{
int tmp1, mask, tmp2, tmp;
mask = 1;
do {
tmp1 = mask;
tmp2 = input;
tmp = input & mask;
input ^= mask;
mask = tmp << 1;
} while (mask);
do {
if (tmp1 != tmp2) {
mask = flag;
flag ^= input;
input = (input & mask) << 1;
}
} while (input);
return flag;
}
实际可以替换成lambda x,y: x + y + 1
实际上这题结构是这样,要求输入code和flag,先检查code和flag的长度与格式
我照这还原了一下,是code长度6字节,范围0-9,flag长度40,开头结尾是DASCTF{}
直接照着伪代码,抽象写了一下
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
/* return flag + 1 + input; */
int core(int flag, int input)
{
int tmp1, mask, tmp2, tmp;
mask = 1;
do {
tmp1 = mask;
tmp2 = input;
tmp = input & mask;
input ^= mask;
mask = tmp << 1;
} while (mask);
do {
if (tmp1 != tmp2) {
mask = flag;
flag ^= input;
input = (input & mask) << 1;
}
} while (input);
return flag;
}
int verification_len()
{
int x = 0;
for (int i = 0;; i++) {
x = core(i, -7);
if (x == 0) {
return i;
}
}
}
char* verification_range(int len)
{
int x;
char* r = calloc(sizeof(char), 100);
int ptr = 0;
for (int i = 32; i < 127; i++) {
x = core(i, -49);
if (x < 0xa && x >= 0) {
// printf("%d\n", i);
r[ptr] = i;
ptr++;
}
}
return r;
}
int flag_len()
{
int x = 0;
for (int i = 0;; i++) {
x = core(i, -41);
if (x == 0) {
return i;
}
}
}
char* flag_part1()
{
char t[] = "DASCTF{}";
int x;
char* r = calloc(sizeof(char), 9);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 32; j < 127; j++) {
x = core(j, ~t[i]);
if (x == 0) {
r[i] = j;
}
}
}
return r;
}
int main()
{
int code_len;
char* ver_code;
char* ver_rang;
code_len = verification_len();
printf("verification code len: %d\n", code_len);
ver_rang = verification_range(code_len);
printf("verification range: %s\n", ver_rang);
code_len = flag_len();
printf("flag len: %d\n", code_len);
ver_code = flag_part1();
printf("flag part1: %s\n", ver_code);
}
得到结果是
verification code len: 6
verification range: 0123456789
flag len: 40
flag part1: DASCTF{}
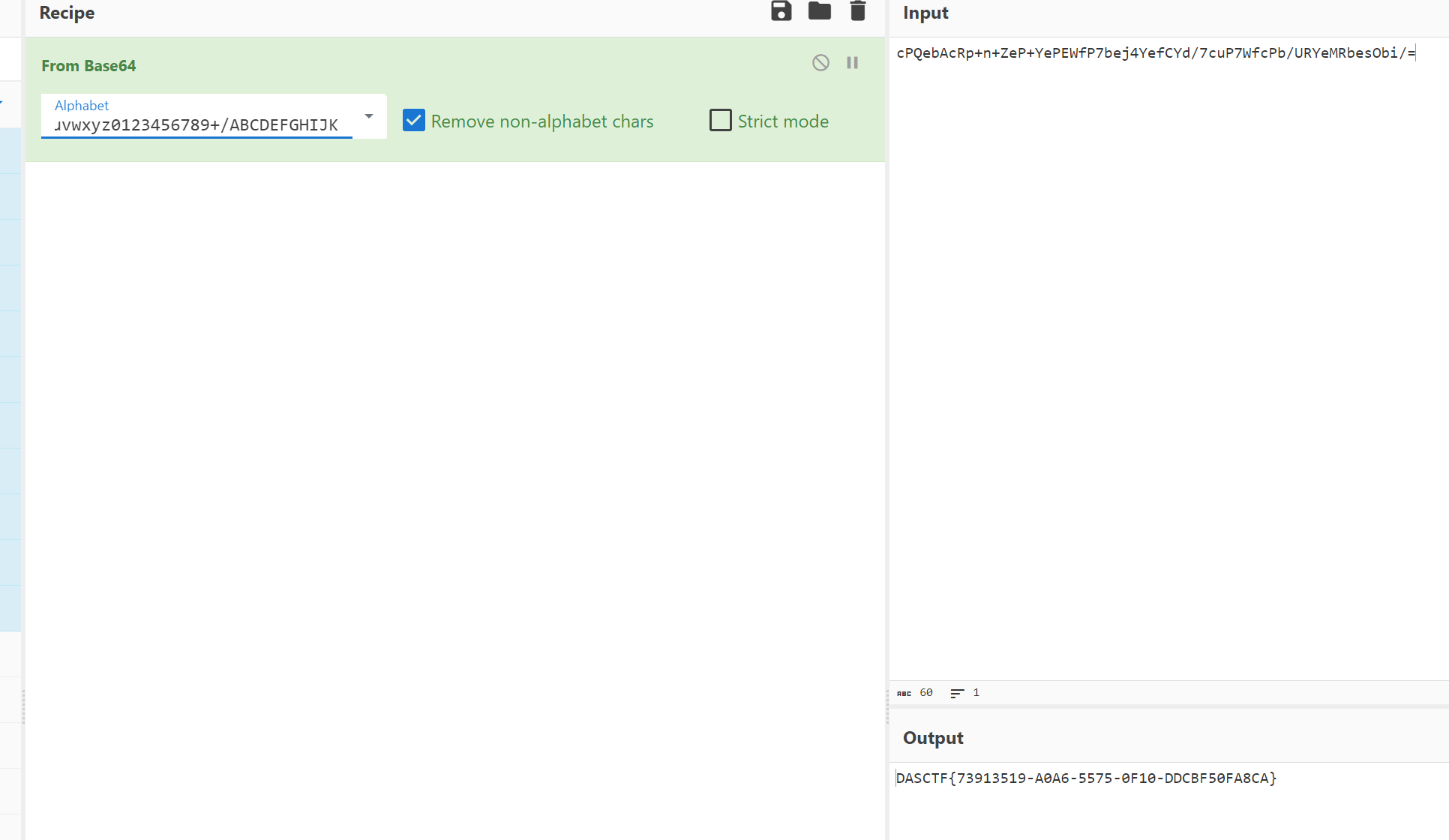
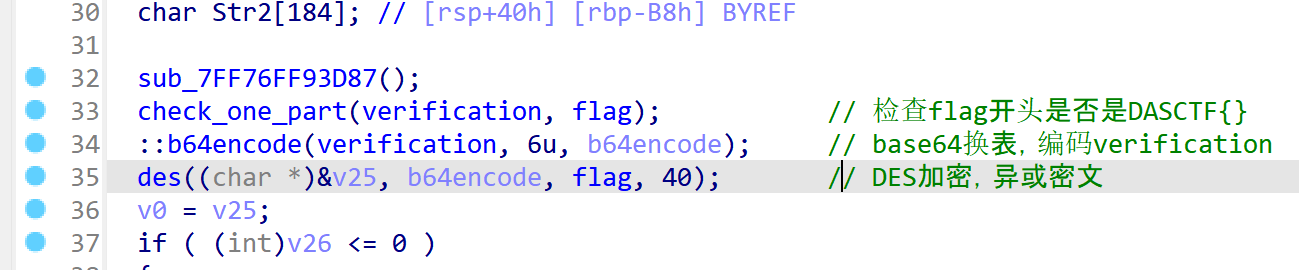
然后code经过了一个base64换表的函数,很明显的换表,没什么好说,把6字节的code变成8字节
然后8字节的code和flag过DES加密,这个DES没改动,加了混淆后很难看,但是DES的表没变,所以很好认出来
DES加密中间还对密文处理了一下
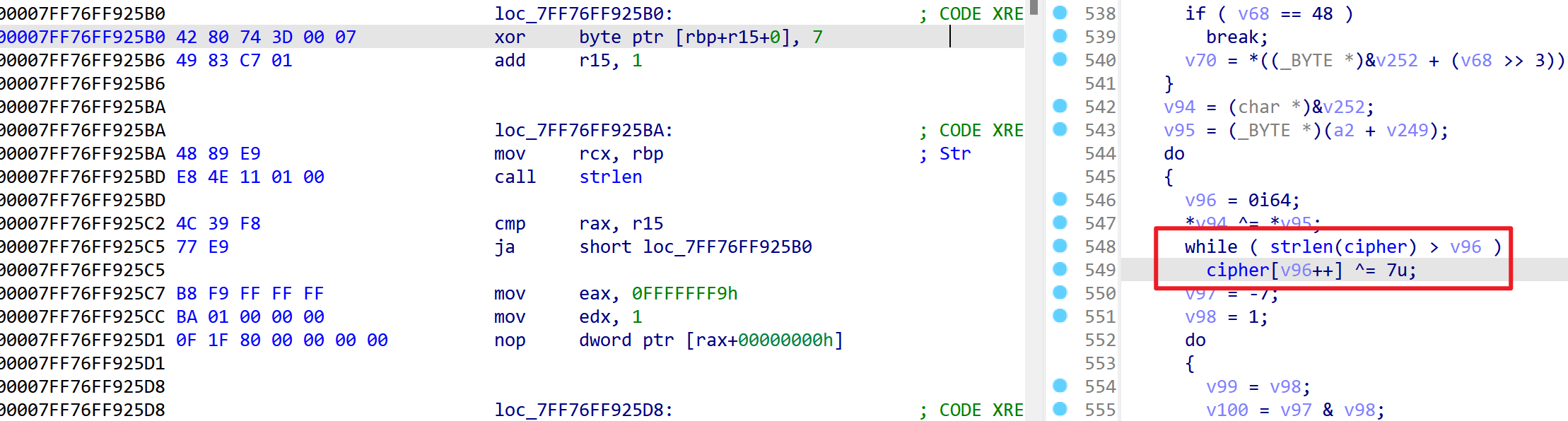
所以整个过程就如下
解密直接爆破code就可以,code6位数,范围0-9,两秒出了
exp:
from base64 import b64encode
import itertools
from string import digits
from Crypto.Cipher import DES
from binascii import unhexlify
def des_descrypt(s, key):
e = DES.new(key, DES.MODE_ECB)
return e.decrypt(unhexlify(s))
def base64_encode(text):
outtab = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/="
intab = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ+/="
text = b64encode(text).decode()
return text.translate(text.maketrans(outtab, intab))
enc = "0723105D5C12217DCDC3601F5ECB54DA9CCEC2279F1684A13A0D716D17217F4C9EA85FF1A42795731CA3C55D3A4D7BEA"
for i in itertools.product(digits, repeat=6):
key = "".join(i)
msg = base64_encode(key.encode())
s = des_descrypt(enc, msg.encode())
if b"DASCTF" in s:
print(key)
print(s)